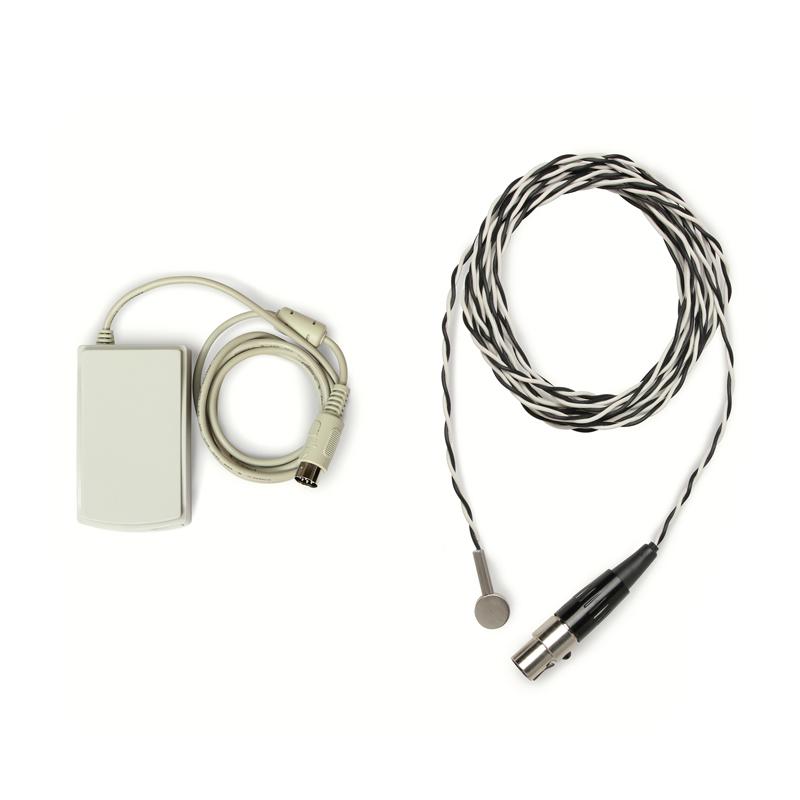
Skin Temperature Kit
Suitable for recording continuous skin temperature on human subjects for biological measurements of temperature in the range of 0°C to 50°C.
Overview
Suitable for recording continuous skin temperature on human subjects for biological measurements of temperature in the range of 0°C to 50°C.
Recommended:
Lt or Lt LabStation: Human Physiology
PowerLab 26T or 15T
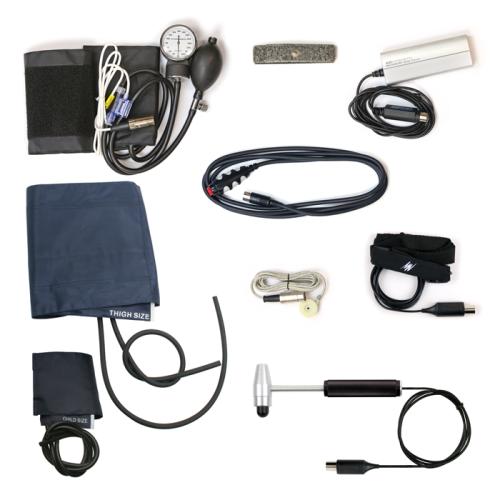
Kit contains:
Support
Support Articles
Our Support Articles contain answers to common questions, how-tos, solutions, and documentation.
Training and Workshops
Maximize time and resources with our customized training services delivered at your facility, on your equipment, on your terms.