20,000 is the average number of breaths a person takes each day - however, it's a vital bodily function that many of us take for granted.
According to the WHO, respiratory diseases are the leading cause of death and disability worldwide - imposing an immense economic burden on our global health care systems. One respiratory disorder that often flies under the radar, but if left untreated, can lead to more serious health problems, is sleep apnea - a condition affecting approximately 1-6% of the adult population. There are three main types of sleep apnea: Obstructive, Central, and Mixed/Complex - of which obstructive sleep apnea is the most common.
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a chronic respiratory disorder characterized by frequent pauses in breathing during sleep. The interruption in airflow is due to upper airway collapse, caused by anatomical predispositions and insufficient neuromuscular compensation. 1-3
Initial side effects of OSA include sleepiness and daytime fatigue. However, research has shown chronic OSA can lead to more concerning health conditions such as high blood pressure, stroke, and even decreased life expectancy. 1,2
Because this syndrome is a combination of anatomical and neuromuscular elements, predicting successful treatment is difficult.4-6
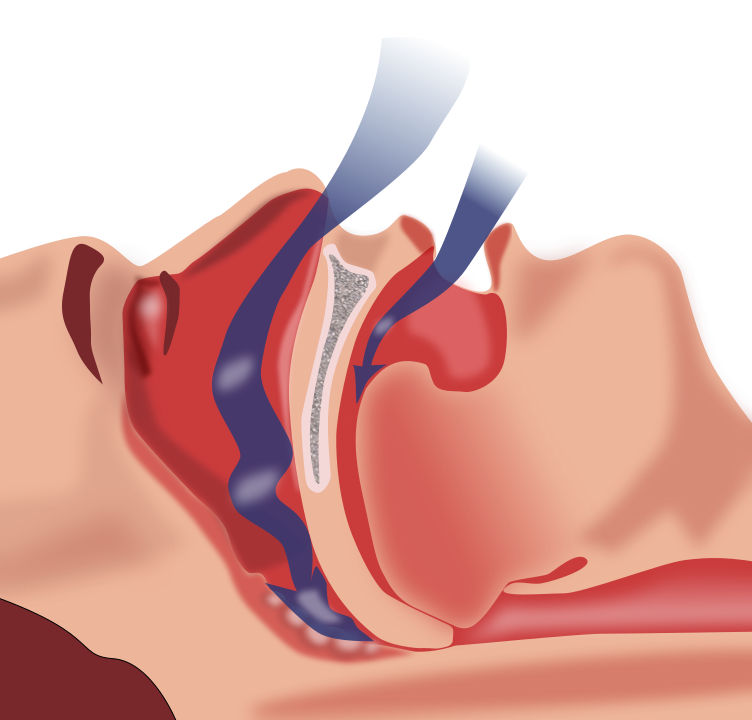
OSA occurs when the muscles in the upper airway collapse during sleep, interrupting airflow to the lungs. Photo Credit: Habib M’henni, Wikimedia Commons.
Millar Mikro-Cath - A high-fidelity catheter for measuring airway pressure
Clinicians looking to treat OSA need the most accurate and unobtrusive means of measuring respiratory data from their patients. Millar’s clinical catheter, the Mikro-Cath, is a highly accurate, FDA and CE-approved catheter specifically designed to measure physiological pressures in the human body.
With the Mikro-Cath, researchers and clinicians can gain insights into the physiology of chronic sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea by studying minute air pressure changes in the pharynx, larynx, and even pleural spaces for up to 24 hours in a patient.
For a detailed overview of the Mikro-Cath and its use in OSA research, check out Millar’s informative video below.
Please note, the Mikro-Cath Pressure Catheter is only available from ADInstruments in North America and Great Britain / Europe regions for research purposes only. For more information about the Mikro-Cath Pressure Catheter or to request a quote - please contact your nearest ADInstruments Representative.
How does the Mikro-Cath compare to Traditional Balloon Catheters?
When comparing the Millar Mikro-Cath to traditional esophageal balloon pressure catheters, the 30% smaller diameter design allows for increased patient comfort and reduced risk of tissue damage when inserting and positioning the device.8
The Mikro-Cath also features the latest sensor-based technology mounted at the tip for highly accurate, true pressure signals at the site of sensor placement.8 This differs from traditional esophageal pressure catheters, where only a mean pressure is calculated along the length of the inflated balloon.7
As the Mikro-Cath does not require any form of inflation - setup, positioning, and signal recording can be more easily achieved.7,8 Furthermore, once the Mikro-Cath is placed, it can be left in situ for up to 24 hours with no requirement for readjustment - which is often not the case with balloon-type catheters.
Finally, because it is a solid-state sensor unaffected by motion or resonance, the Mikro-Cath has been validated for studying laryngeal pressures during exercise and vocal cord contact pressures.
Related: Three unique research applications of the Millar Pressure Catheter »
Moreover, the Millar Mikro-Cath is a highly sensitive, solid-state sensor-based catheter that excels at accurately measuring low pressures not only in airway applications but in cardiovascular and intra-compartmental pressure research as well.
For more information about the Mikro-Cath and its research applications, or to request a quote - please contact your nearest ADInstruments Representative. Note, the Mikro-Cath Pressure Catheter is only available from ADInstruments in North America and Great Britain / Europe regions for research purposes only.
ADInstruments and Millar
With over 50 years of innovating pressure sensor technology, Millar is the world leader in pressure sensor solutions.
By combining Millar’s highly sensitive, minimally invasive catheters with the precision of PowerLab data acquisition and LabChart data analysis software, you can build a high quality, flexible system that will give you comprehensive data you can trust.
We are proud to partner with Millar to support researchers around the world, and are also the exclusive global distributors of Millar Mikro-Tip pressure catheters and associated hardware for ventricular pressure-volume and invasive pressure recording.
Related Resources:
- Caring for your Millar Catheter - Best Practice Tips »
- How to Calibrate a Millar Catheter using the Pressure Gauge Kit »
- How to Calibrate a Millar Catheter Using the Delta-Cal Electronic Pressure Simulator »
References:
1. Punjabu, N.M. The Epidemiology of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society, no.2 (2008): 126-143.
2. Young, T. et al. Epidemiology of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population Health Perspective. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 165, no.9 (2002): 1217-1239
3. Oliven, R. et al. Alteration in upper airway dilator muscle activation during sleep: comparison of patients with obstructive sleep apnea and healthy subjects. Journal of Applied Physiology 124, mo.2 (2018): 421-429
4. Le, T.B. et al. Airflow limitation in a collapsible model of the human pharynx: physical mechanisms studies with fluid-structure interaction simulations and experiments." Physiological reposts 7, no. 10 (2019): e12099
5. El-Chami, M. et al. Exposure to intermittent hypoxia and sustained hypercapnia reduces therapeutic CPAP in participants with obstructive sleep apnea. Journal of Applied Physiology 123, no.4 (2017): 993-1002
6. Eckert, D. et al. Central sleep apnea: pathophysiology and treatment. Chest 131, no.2 (2007): 595-607
7. CooperSurgical. Feb. 2014. Adult esophageal balloon catheter instructions for use. Trumbull, CT, USA. https://www.coopersurgical.com/detail/esophageal-balloon-catheter-set/ (Accessed 2 July 2020)
8. Millar Inc. 2013. Mikro-Cath Pressure Catheter Instructions of Use. Houston, TX, USA. https://millar.com/Knowledge-Center/ (Accessed 2 July 2020)


