A step-by-step demonstration of how to calibrate a Millar Pressure Catheter using a Pressure Gauge Kit.
Equipment required
- Millar Pressure Catheter
- Catheter Interface Cable
- Hemostatic Valve (e.g. Tuohy Borst Adapter)
- Pressure Gauge Kit (includes syringes, tubing, and a manometer dial)
- Warm Saline
- Bridge Amp
- PowerLab
- Computer with LabChart Software installed
Procedure
Equipment set-up
Before recording any signals, it’s important to set up your data acquisition equipment correctly.
- First, connect the catheter to the Bridge Amp using the Catheter Interface Cable
- Connect the Bridge Amp to the PowerLab
- Lastly, connect the PowerLab to your computer and open LabChart
Presoak Catheter Tip
Fill the hemostatic valve with saline
Next, the hemostatic valve needs to be filled with warm saline. To do this:
- Fill a syringe with warm saline.
- Twist open the valve.
- Remove the red cap on top of the valve and connect the saline-filled syringe.
- Block off the remaining end that has the connector attachment with your finger and slowly start to introduce the saline.
- Once full, close off the valve and connect the manometer to the end previously blocked by your finger.
- Lastly, disconnect the syringe from the top, leaving it open to the air.
Insert Catheter into hemostatic valve
Now you are ready to insert the catheter into the valve. For this:
- Once again, open up the valve. Make sure it is completely open.
- Carefully insert the pre-soaked catheter inside the valve, into the saline.
- Close off the valve to create a seal around the catheter. Make sure you don’t screw it too tight, or you can damage the catheter.
Zero the Catheter
Now that the catheter has been inserted into the valve and it is open to the atmospheric pressure (via the top opening), you can zero the transducer.
- In LabChart, click on the channel name that the Bridge Amp is connected to and select ‘Bridge Amp’ from the drop-down menu.
- In the Bridge Amp Dialog make sure that the range is sufficient for the pressures you are recording. In this case, 10 mV will be fine.
Tip: Care must be taken when determining an appropriate range for your pressure transducer. If the range is too large, the resolution will be poor and small fluctuations will not be seen. Conversely, if the range is too small, the signal will go out of range and you will lose data. Millar Catheters have an excitation of 5V, resulting in an output of ~ 2.5 mV/100 mmHg.
- Next, zero the transducer by clicking ‘Zero’. This will take a couple of seconds, make sure that the transducer is not moved during this period
- Once that is done, click ‘OK’
Calibrate the Catheter
Once the transducer has been zeroed, you are now ready to calibrate the transducer. This is done by recording two pressures of known value and using these to perform a two-point calibration.
- First, start the recording in LabChart by clicking the ‘Start’ button
- Because the catheter has just been zeroed, we know that the reading on-screen is equal to 0 mmHg. Enter a comment labelled ‘0’ into LabChart to mark this section of the recording.
- Next, re-connected the saline-filled syringe, and slowly increase the pressure by pushing down on the syringe. You should see the pressure reading on the manometer go up (See image below for example of what the set-up should look like).
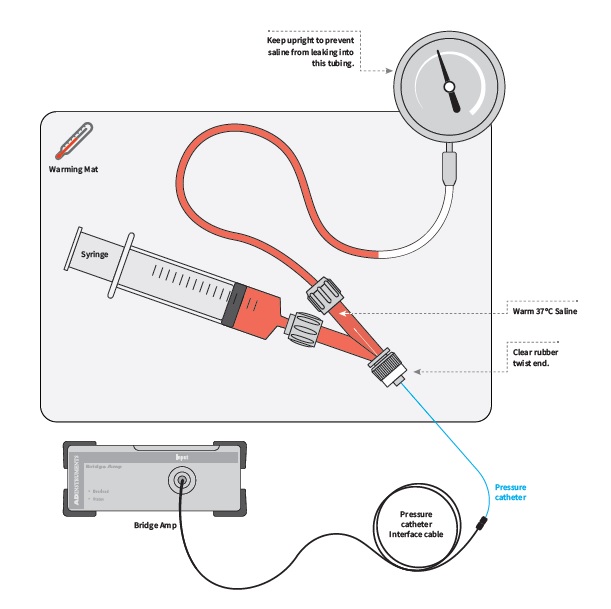
- Increase the pressure until 100 mmHg is reached, and drop another comment into LabChart labeled 100.
- Click ‘Stop’ to stop the recording
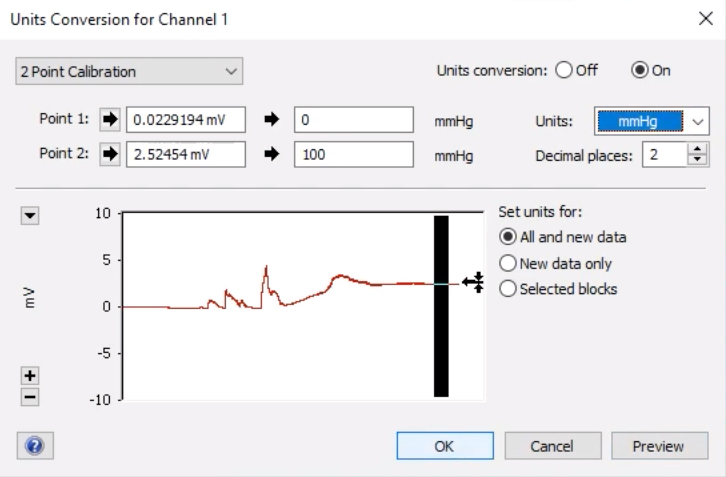
Units Conversion
- Make a selection of the recording between the two comments by clicking and dragging the mouse across the recording.
- Click on the Channel name and go to ‘Units Conversion’. The Units Conversion Dialog will display the recording that was selected (see image below).
- Select an area of the recording that represents the first pressure reading in the preview window.
- Then click the arrow next to Point 1 and the voltage for that pressure will be entered into the left-hand box.
- Next, type in the pressure value this selection represents in the right-hand box (in this case, 0).
- Repeat the above steps for the second pressure recording of 100, for Point 2.
- Make sure the units are set as mmHg, then click ‘OK’.
- You now have a calibrated catheter!
Additional Resources:
How to Calibrate a Millar Catheter Using the DeltaCal Electronic Pressure Simulator »
Troubleshooting your Millar Catheter: Three common problems and how to fix them »
Best Practice Tips for maximizing the life of your Millar Catheter »
Surgical Instruction Videos:
Left Ventricular Pressure via Carotid in Rat »
Left Ventricular Pressure via Carotid in Mouse »
Best Practices for Surgical Procedures with Millar Catheters »