Kaha Sciences fully implantable rat and mouse telemetry solutions combine state of the art technologies to provide unrivaled accuracy and long-term recording in neuroscience research.
With options to measure physiological pressures, biopotentials, sympathetic nerve activity, and tissue oxygen concentrations, 24/7 over the course of your experiment - Kaha Sciences telemeters allow you to measure a range of physiological signals to meet your research needs.
Below we have outlined some unique neuroscience applications using Kaha Sciences telemeters, plus some of the benefits they provide over other available technologies.
Kaha Sciences Telemetry – Neuroscience applications:
Intracranial Pressure
Kaha Sciences rat pressure telemeters use the Millar Mikro-Tip® solid-state sensor technology, at the catheter tip to accurately measure small pressures, repeatably and with high fidelity. The 2 Fr (0.66 mm) sensor can be implanted in the epidural or subdural space for measurement of intracranial pressure. Telemeters are available with single 25cm catheters (TRM54P), dual catheters (TRM54PP), or in combination with a biopotential channel (TRM54PB).
Related: Benefits of using solid-state pressure sensors »
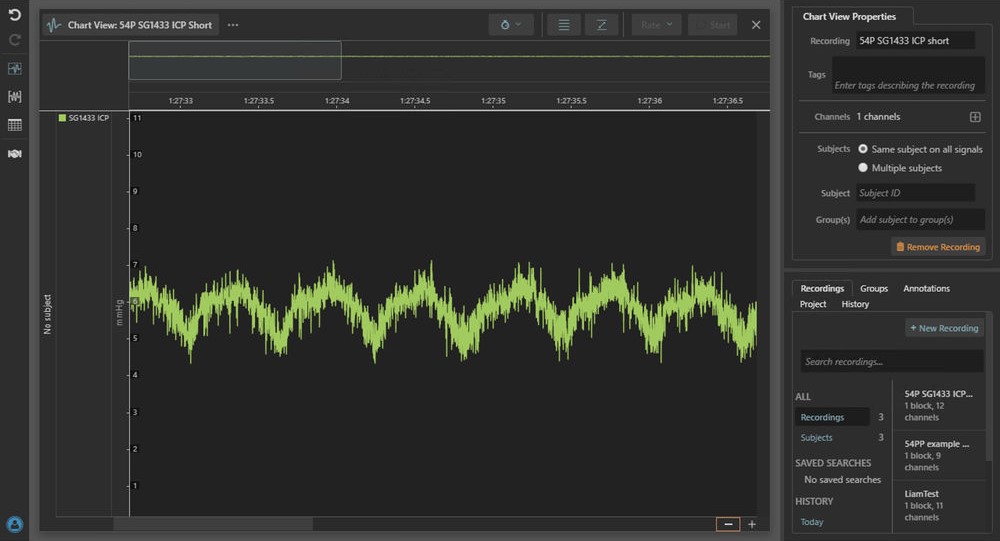
Intracranial pressure recording using the Pressure Telemeter in LabChart Lightning.
Publications:
- Thakkar, P. et al. Hypertensive Response to Ischemic Stroke in the Normotensive Wistar Rat: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance. Stroke 50, 2522–2530 (2019).
- Kawoos, U et al. Protective Effect of N-Acetylcysteine Amide on Blast-Induced Increase in Intracranial Pressure in Rats. Frontiers in Neurology, 8, 219 (2017)
Related: Long-term monitoring of ICP in freely moving rats (webinar) »
Epilepsy
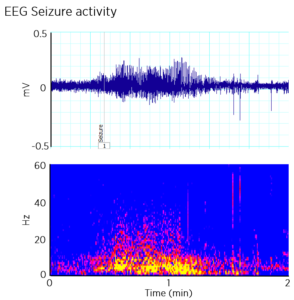
Monitoring pathophysiological activity, such as epileptic seizure, in vivo has traditionally been challenging due to the spontaneous nature of the condition. Kaha Sciences’ innovative use of wireless power technology has removed the compromise of battery-life to allow users to record continuously at a high sampling rate (2kHz) over long-term experiments.
The reusable rat biopotential telemeters give users the option to record a single EEG channel (TR50B) or combine EEG and nuchal EMG recordings (TR50BB), while our mouse telemeters (MT10B) allow the recording of EEG along with activity. The ability to record continuously ensures that more data is captured and fewer seizure events are missed.
Publications:
- Hill, A. C., et al. Correction of medication nonadherence results in better seizure outcomes than dose escalation in a novel preclinical epilepsy model of adherence. Epilepsia 60 (3), 475-484 (2019).
- Read, M. I., et al. Atenolol offers better protection than clonidine against cardiac injury in kainic acid‐induced status epilepticus. British Journal of Pharmacology 172 (19), 4626-4638 (2016).
Sleep and Circadian Rhythm
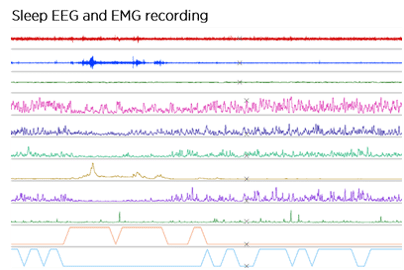
The ability to capture data in real-time, 24/7 is invaluable in studying normal physiological rhythms over long experimental time courses. Using the Kaha Sciences rat (TR50B and TR50BB) and mouse (MT10B) biopotential telemeters it’s possible to record EEG or EMG and identify different stages in the sleep/wake cycle.
Alternatively, users can benefit from the full range of Kaha telemeters to investigate ultradian or circadian rhythms in physiological parameters and how these might change in disease.
Publications:
Tissue oxygen
The TR57Y tissue oxygen telemeter is the only device available on the market that can measure long-term tissue oxygen concentration from conscious rats, in real-time. The telemeter uses a stable carbon paste electrode and can measure local ischemia and tissue metabolic activity in the brain or kidney. Combined with our wireless power technology researchers have been able to assess circadian variability in kidney tissue oxygen thanks to the ability to record 24/7.
Find out more: Tissue oxygen telemetry: How does it work and why is it beneficial to your research? »
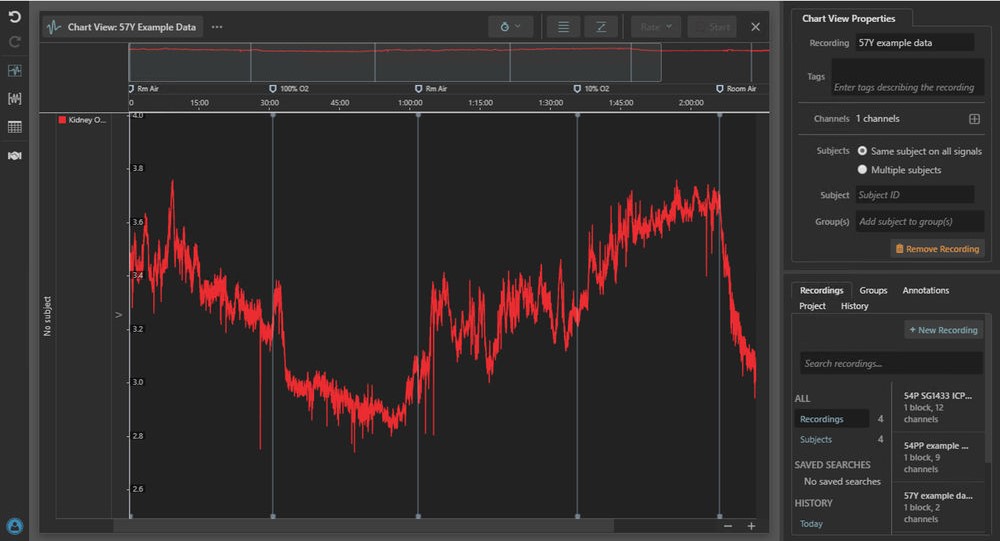
Kidney tissue oxygen measurement using the Tissue Oxygen Telemeter in LabChart Lightning.
Publications:
- Adamovich, Y. et al. Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Rhythms Are Circadian Clock Controlled and Differentially Directed by Behavioral Signals. Cell Metab. 29, 1092-1103.e3 (2019).
- Russel, D, M. et al. A fully implantable telemetry system for the chronic monitoring of brain tissue oxygen in freely moving rats Journal Article. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 204 (2), 242-248 (2012)
Sympathetic Nerve Activity (SNA)
The TRM56SP telemeters allow users to simultaneously record SNA and blood pressure to give an insight into the autonomic control of cardiovascular physiology. The input range of the SNA leads is ±60µV making it ideal for activity recording from fine, peripheral autonomic nerves studies in studies of stress, cardiovascular control and the development of hypertension.
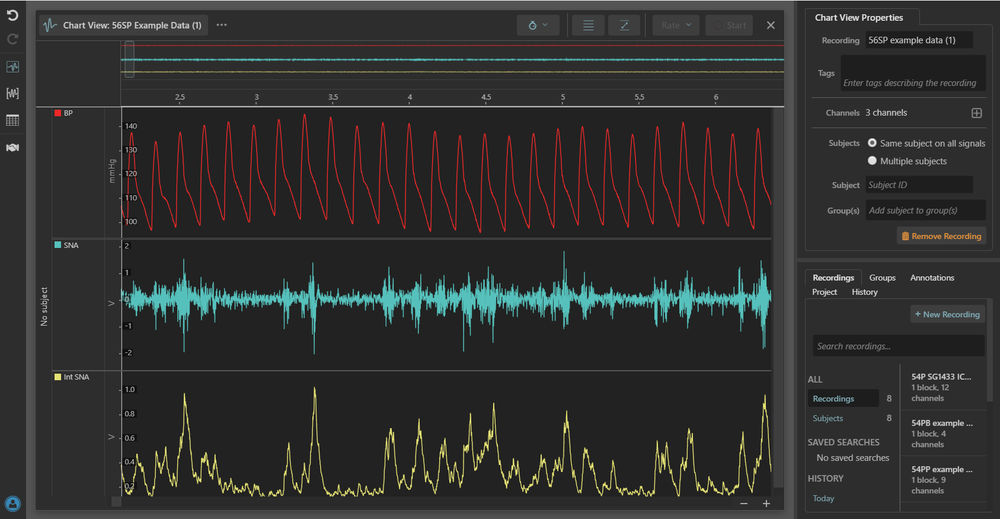
Sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) and Blood pressure (BP) recordings using the TRM56SP telemeter in LabChart Lightning.
Publications:
For more information about Kaha Sciences telemeters, or to discuss your specific research application please contact your nearest ADInstruments support representative.
Related resources:
Four benefits of telemetry for research »
Kaha Telemeters Cardiovascular Applications »
Exploring ICP, Tissue Oxygenation and RSNA with Implantable Telemetry »
How to measure chronic intracranial pressure measurements in rats »
Tips for handling and analyzing large telemetry data sets »
Kaha telemeters: Surgical Videos and Webinars »
